兰州网站定制公司网站推广 软件
系列文章目录
【时间序列篇】基于LSTM的序列分类-Pytorch实现 part1 案例复现
【时间序列篇】基于LSTM的序列分类-Pytorch实现 part2 自有数据集构建
【时间序列篇】基于LSTM的序列分类-Pytorch实现 part3 化为己用
在一个人体姿态估计的任务中,需要用深度学习模型来进行序列分类。
化为己用,实现成功。
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- 一、模型训练
- 1 导入库和自用函数
- 2 导入数据集
- 3 设备部署
- 4 网络模型
- 5 训练过程
- 6 运行结果
- 7 完整代码
- SequenceClassifier
- 二、模型预测
- 1 完整代码
- 2 运行结果
- 三、模型评估
- 1 完整代码
- 2 运行结果
- 总结
前言
结合了part1 和 part2的文章,处理现有序列分类任务。
基于LSTM的序列分类-Pytorch实现 这个部分先告一段落。
part3 主要是优化后的代码实现,包括训练,预测,模型评估。
一、模型训练
这一部分就是对part1文章中代码的优化和运行结果。每一节都是一整个代码的一部分,最后放完整代码。
1 导入库和自用函数
import os
import copy
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from tqdm import tqdmdef calculate_accuracy(y_pred, y_true):_, predicted_labels = torch.max(y_pred, 1)correct = (predicted_labels == y_true).float()accuracy = correct.sum() / len(correct)return accuracy
2 导入数据集
'''
/****************************************************/导入数据集
/****************************************************/
'''
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 路径指定
# ----------------------------------------------------#
ROOT_PATH = "DATA/RT_Position_dataset"dataset_path = os.path.join(ROOT_PATH, "dataset")
target_path = os.path.join(ROOT_PATH, "groups/Movement4_target.csv")
groups_path = os.path.join(ROOT_PATH, "groups/Movement4_DatasetGroup.csv")checkpoint_pth = "best_model.pth" # 模型参数
seq_len = 16 # 序列长度
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# sequences列表读取所有的样本
# ----------------------------------------------------#
path = os.path.join(dataset_path, "Movement4_")
sequences = list()
for i in range(1, 3731): # 3731为样本数file_path = path + str(i) + '.csv'# print(file_path)df = pd.read_csv(file_path, header=0)values = df.valuessequences.append(values)# print(len(sequences))
# len_sequences = []
# for one_seq in sequences:
# len_sequences.append(len(one_seq))
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 数据集标签
# ----------------------------------------------------#
targets = pd.read_csv(target_path)
targets = targets.values[:, 1]
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 数据集划分
# ----------------------------------------------------#
groups = pd.read_csv(groups_path, header=0)
groups = groups.values[:, 1]# ----------------------------------------------------#
# Padding the sequence with the values in last row to max length
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 函数用于填充和截断序列
def pad_truncate_sequences(sequences, max_len, dim=4, truncating='post', padding='post'):# 初始化一个空的numpy数组,用于存储填充后的序列padded_sequences = np.zeros((len(sequences), max_len, dim))for i, one_seq in enumerate(sequences):if len(one_seq) > max_len: # 截断if truncating == 'pre':padded_sequences[i] = one_seq[-max_len:]else:padded_sequences[i] = one_seq[:max_len]else: # 填充padding_len = max_len - len(one_seq)to_concat = np.repeat(one_seq[-1], padding_len).reshape(dim, padding_len).transpose()if padding == 'pre':padded_sequences[i] = np.concatenate([to_concat, one_seq])else:padded_sequences[i] = np.concatenate([one_seq, to_concat])return padded_sequences# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 设置序列长度
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 使用自定义函数进行填充和截断
final_seq = pad_truncate_sequences(sequences, max_len=seq_len, dim=4, truncating='post', padding='post')# 设置标签从 1~6 换为 0~5
targets = np.array(targets)
final_targets = targets - 1# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 数据集划分
# ----------------------------------------------------## 将numpy数组转换为PyTorch张量
final_seq = torch.tensor(final_seq, dtype=torch.float)# 划分样本为 训练集,验证集
train = [final_seq[i] for i in range(len(groups)) if groups[i] == 1]
validation = [final_seq[i] for i in range(len(groups)) if groups[i] == 2]
# 标签同理
train_target = [final_targets[i] for i in range(len(groups)) if groups[i] == 1]
validation_target = [final_targets[i] for i in range(len(groups)) if groups[i] == 2]# 转换为PyTorch张量
train = torch.stack(train)
train_target = torch.tensor(train_target).long()validation = torch.stack(validation)
validation_target = torch.tensor(validation_target).long()
3 设备部署
'''
/****************************************************/device
/****************************************************/
'''def device_on():device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")print(f"Using {device} device")return device# ----------------------------------------------------#
# device
# ----------------------------------------------------#
device = device_on()
4 网络模型
'''
/****************************************************/网络模型
/****************************************************/
'''# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 创建模型
# ----------------------------------------------------#
class TimeSeriesClassifier(nn.Module):def __init__(self, n_features, hidden_dim=256, output_size=1):super().__init__()self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=n_features, hidden_size=hidden_dim, batch_first=True)self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_size) # output_size classesdef forward(self, x):x, _ = self.lstm(x) # LSTM层x = x[:, -1, :] # 只取LSTM输出中的最后一个时间步x = self.fc(x) # 通过一个全连接层return x# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 模型实例化
# ----------------------------------------------------#
seq_len = 16 # 根据你的序列长度进行调整
n_features = 4 # 根据你的特征数量进行调整
output_size = 6
model = TimeSeriesClassifier(n_features=n_features, output_size=output_size)# # 打印模型结构
print(model)
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 模型部署
# ----------------------------------------------------#
model.to(device)
5 训练过程
'''
/****************************************************/训练过程
/****************************************************/
'''# 设置训练参数
epochs = 100 # 训练轮数,根据需要进行调整
batch_size = 4 # 批大小,根据你的硬件调整# DataLoader 加载数据集
train_dataset = torch.utils.data.TensorDataset(train, train_target)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)validation_dataset = torch.utils.data.TensorDataset(validation, validation_target)
validation_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=validation_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)# 定义损失函数和优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
criterion = criterion.to(device)# 学习率和优化策略
learning_rate = 1e-3
optimizer = optim.Adam(params=model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate, weight_decay=5e-4)
lr_scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=2, gamma=0.5) # 设置学习率下降策略# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 训练
# ----------------------------------------------------#
best_acc = 0.0
for epoch in range(epochs):model.train() # 将模型设置为训练模式train_epoch_loss = []train_epoch_accuracy = []pbar = tqdm(train_loader, total=len(train_loader))for index, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(pbar, start=1):# 获取输入数据和目标,并将它们转移到GPU(如果可用)inputs = inputs.to(device)labels = labels.to(device)# 清零梯度optimizer.zero_grad()# 前向传播outputs = model(inputs)loss = criterion(outputs, labels)loss.backward()optimizer.step()train_epoch_loss.append(loss.item())accuracy = calculate_accuracy(outputs, labels)train_epoch_accuracy.append(accuracy.item())pbar.set_description(f'Epoch [{epoch + 1}/{epochs}]')pbar.set_postfix(**{'loss': loss.item(),'accuracy': accuracy.item(),})# Validation accuracymodel.eval()valid_epoch_loss = []valid_epoch_accuracy = []pbar = tqdm(validation_loader, total=len(validation_loader))for index, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(pbar, start=1):inputs = inputs.to(device)labels = labels.to(device)outputs = model(inputs)loss = criterion(outputs, labels)valid_epoch_loss.append(loss.item())accuracy = calculate_accuracy(outputs, labels)valid_epoch_accuracy.append(accuracy.item())pbar.set_description('valid')pbar.set_postfix(**{'total_loss': loss.item(),'accuracy': accuracy.item(),})# 计算平均精度print("--------------------------------------------")train_epoch_loss = np.average(train_epoch_loss)train_epoch_accuracy = np.average(train_epoch_accuracy)print(f'Epoch {epoch + 1}, train Accuracy: {train_epoch_accuracy:.4f}')valid_epoch_loss = np.average(valid_epoch_loss)valid_epoch_accuracy = np.average(valid_epoch_accuracy)print(f'Epoch {epoch + 1}, Validation Accuracy: {valid_epoch_accuracy:.4f}')print("--------------------------------------------")if valid_epoch_accuracy > best_acc:best_acc = valid_epoch_accuracybest_model_wts = copy.deepcopy(model.state_dict())state = {'state_dict': model.state_dict(),'best_acc': best_acc,'optimizer': optimizer.state_dict(),}torch.save(state, checkpoint_pth)print('Finished Training')
print('Best val Acc: {:4f}'.format(best_acc))
6 运行结果


可以看到相比起part1的实验,分类准确率更高。毕竟part1总共314个样本,自有数据集样本有3730个。
7 完整代码
SequenceClassifier
二、模型预测
输入样本,运行模型,输出预测
1 完整代码
这里直接贴完整代码。
"""
@file name:predict.py
@desc: 用于序列分类预测
"""import os
import pandas as pd
import torch
import torch.nn as nn'''
/****************************************************/输入一个数据样本
/****************************************************/
'''
# 读取CSV样本文件
csv_file = "DATA/RT_Position_dataset/dataset/Movement4_7.csv"
data = pd.read_csv(csv_file)# 将Pandas DataFrame转换为NumPy数组
data_array = data.values# 将NumPy数组转换为PyTorch张量
input = torch.tensor(data_array, dtype=torch.float).unsqueeze(0)'''
/****************************************************/device
/****************************************************/
'''def device_on():device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")print(f"Using {device} device")return device# ----------------------------------------------------#
# device
# ----------------------------------------------------#
device = device_on()'''
/****************************************************/网络模型
/****************************************************/
'''# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 创建模型
# ----------------------------------------------------#
class TimeSeriesClassifier(nn.Module):def __init__(self, n_features, hidden_dim=256, output_size=1):super().__init__()self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=n_features, hidden_size=hidden_dim, batch_first=True)self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_size) # output_size classesdef forward(self, x):x, _ = self.lstm(x) # LSTM层x = x[:, -1, :] # 只取LSTM输出中的最后一个时间步x = self.fc(x) # 通过一个全连接层return x# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 模型实例化
# ----------------------------------------------------#
seq_len = 16 # 根据你的序列长度进行调整
n_features = 4 # 根据你的特征数量进行调整
output_size = 6
model = TimeSeriesClassifier(n_features=n_features, output_size=output_size)# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 模型部署
# ----------------------------------------------------#
model.to(device)# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 导入模型参数
# ----------------------------------------------------#
save_pth = "best_model.pth"
checkpoint = torch.load(save_pth)
best_acc = checkpoint['best_acc']
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
'''
/****************************************************/预测输出
/****************************************************/
'''
model.eval() # 设置为评估模式# 假设你有一个预处理好的序列数据,shape为(batch_size, seq_len, n_features)
# 例如:一个序列,长度为16,每个时间步有4个特征
# input = torch.randn(1, 16, 4) # 替换为你的数据with torch.no_grad():output = model(input)# 将输出转换为概率分布prediction = torch.softmax(output, dim=1)# 取得最高概率的类别作为预测结果predicted_class = torch.argmax(prediction, dim=1)
print(f"Predicted class: {predicted_class}")2 运行结果
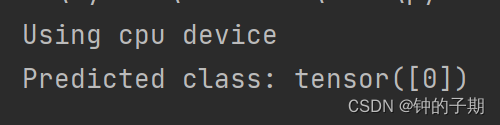
三、模型评估
1 完整代码
"""
@file name:evaluate.py
@desc: 用于模型评估
"""import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, precision_score, recall_score, f1_scoredef calculate_accuracy(y_pred, y_true):_, predicted_labels = torch.max(y_pred, 1)correct = (predicted_labels == y_true).float()accuracy = correct.sum() / len(correct)return accuracy'''
/****************************************************/导入数据集
/****************************************************/
'''
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 路径指定
# ----------------------------------------------------#
ROOT_PATH = "DATA/RT_Position_dataset"dataset_path = os.path.join(ROOT_PATH, "dataset")
target_path = os.path.join(ROOT_PATH, "groups/Movement4_target.csv")
groups_path = os.path.join(ROOT_PATH, "groups/Movement4_DatasetGroup.csv")checkpoint_pth = "best_model.pth" # 模型参数
seq_len = 16 # 序列长度
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# sequences列表读取所有的样本
# ----------------------------------------------------#
path = os.path.join(dataset_path, "Movement4_")
sequences = list()
for i in range(1, 3731): # 3731为样本数file_path = path + str(i) + '.csv'# print(file_path)df = pd.read_csv(file_path, header=0)values = df.valuessequences.append(values)# print(len(sequences))
# len_sequences = []
# for one_seq in sequences:
# len_sequences.append(len(one_seq))
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 数据集标签
# ----------------------------------------------------#
targets = pd.read_csv(target_path)
targets = targets.values[:, 1]
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 数据集划分
# ----------------------------------------------------#
groups = pd.read_csv(groups_path, header=0)
groups = groups.values[:, 1]# ----------------------------------------------------#
# Padding the sequence with the values in last row to max length
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 函数用于填充和截断序列
def pad_truncate_sequences(sequences, max_len, dim=4, truncating='post', padding='post'):# 初始化一个空的numpy数组,用于存储填充后的序列padded_sequences = np.zeros((len(sequences), max_len, dim))for i, one_seq in enumerate(sequences):if len(one_seq) > max_len: # 截断if truncating == 'pre':padded_sequences[i] = one_seq[-max_len:]else:padded_sequences[i] = one_seq[:max_len]else: # 填充padding_len = max_len - len(one_seq)to_concat = np.repeat(one_seq[-1], padding_len).reshape(dim, padding_len).transpose()if padding == 'pre':padded_sequences[i] = np.concatenate([to_concat, one_seq])else:padded_sequences[i] = np.concatenate([one_seq, to_concat])return padded_sequences# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 设置序列长度
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 使用自定义函数进行填充和截断
final_seq = pad_truncate_sequences(sequences, max_len=seq_len, dim=4, truncating='post', padding='post')# 设置标签从 1~6 换为 0~5
targets = np.array(targets)
final_targets = targets - 1# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 数据集划分
# ----------------------------------------------------## 将numpy数组转换为PyTorch张量
final_seq = torch.tensor(final_seq, dtype=torch.float)# 划分样本为 训练集,验证集
train = [final_seq[i] for i in range(len(groups)) if groups[i] == 1]
validation = [final_seq[i] for i in range(len(groups)) if groups[i] == 2]
# 标签同理
train_target = [final_targets[i] for i in range(len(groups)) if groups[i] == 1]
validation_target = [final_targets[i] for i in range(len(groups)) if groups[i] == 2]# 转换为PyTorch张量
train = torch.stack(train)
train_target = torch.tensor(train_target).long()validation = torch.stack(validation)
validation_target = torch.tensor(validation_target).long()'''
/****************************************************/device
/****************************************************/
'''def device_on():device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")print(f"Using {device} device")return device# ----------------------------------------------------#
# device
# ----------------------------------------------------#
device = device_on()'''
/****************************************************/网络模型
/****************************************************/
'''# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 创建模型
# ----------------------------------------------------#
class TimeSeriesClassifier(nn.Module):def __init__(self, n_features, hidden_dim=256, output_size=1):super().__init__()self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=n_features, hidden_size=hidden_dim, batch_first=True)self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_size) # output_size classesdef forward(self, x):x, _ = self.lstm(x) # LSTM层x = x[:, -1, :] # 只取LSTM输出中的最后一个时间步x = self.fc(x) # 通过一个全连接层return x# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 模型实例化
# ----------------------------------------------------#
seq_len = 16 # 根据你的序列长度进行调整
n_features = 4 # 根据你的特征数量进行调整
output_size = 6
model = TimeSeriesClassifier(n_features=n_features, output_size=output_size)# # 打印模型结构
print(model)
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 模型部署
# ----------------------------------------------------#
model.to(device)# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 导入模型参数
# ----------------------------------------------------#
checkpoint_pth = "best_model.pth"
checkpoint = torch.load(checkpoint_pth)
best_acc = checkpoint['best_acc']
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
batch_size = 4# DataLoader 加载数据集
train_dataset = torch.utils.data.TensorDataset(train, train_target)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)validation_dataset = torch.utils.data.TensorDataset(validation, validation_target)
validation_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=validation_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)'''
/****************************************************/模型评估
/****************************************************/
'''
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 评估
# ----------------------------------------------------## Validation
model.eval()
# 存储所有预测和真实标签
all_preds = []
all_labels = []
# 不计算梯度,减少计算和内存消耗
with torch.no_grad():for data, labels in validation_loader:# data和labels的预处理(如:转移到GPU、标准化等)...# 生成预测并获取最可能的类别outputs = model(data)_, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1)# 收集预测和真实标签all_preds.extend(predicted.cpu().numpy())all_labels.extend(labels.cpu().numpy())# 计算性能指标
accuracy = accuracy_score(all_labels, all_preds)
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(all_labels, all_preds)
precision = precision_score(all_labels, all_preds, average='macro')
recall = recall_score(all_labels, all_preds, average='macro')
f1 = f1_score(all_labels, all_preds, average='macro')print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy}")
print(f"Confusion Matrix:\n{conf_matrix}")
print(f"Precision: {precision}")
print(f"Recall: {recall}")
print(f"F1 Score: {f1}")2 运行结果
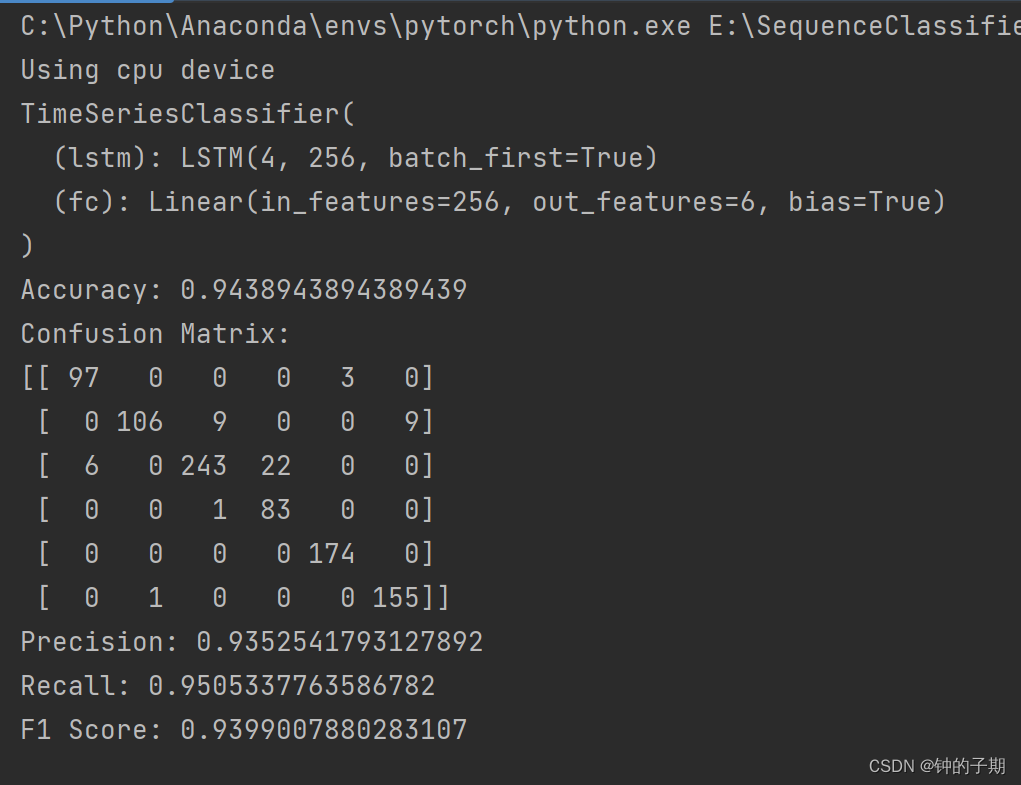
总结
到此,基于LSTM的序列分类任务就结束啦。
完整项目
SequenceClassifier
