桂林 网站建站专做皮鞋销售网站
1、在需要运行的jar包同级目录下建立启动脚本文件:
文件内容:
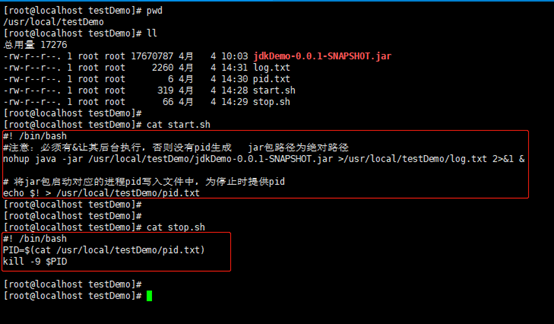
#! /bin/bash
#注意:必须有&让其后台执行,否则没有pid生成 jar包路径为绝对路径
nohup java -jar /usr/local/testDemo/jdkDemo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar >/usr/local/testDemo/log.txt 2>&1 &
# 将jar包启动对应的进程pid写入文件中,为停止时提供pid
echo $! > /usr/local/testDemo/pid.txt
2、同理建立停止脚本文件 stop.sh,文件内容:
#! /bin/bash
PID=$(cat /usr/local/testDemo/pid.txt)
kill -9 $PID
建立好之后如图:
然后启动jar包命令:
./start.sh
停止jar包命令:
./stop.sh
查看jar包日志命令(在jar包同级目录或文件加上目录):
tail –f log.txt
启动后查看jar包是否运行:
ps -ef | grep java

参考:Linux以nohup方式运行jar包-软件开发-老麻
