上海网站建设网页济宁外贸网站建设
核对是保障资金安全的重要机制。
时效角度,主要有:
(准)实时核对
准确性不如离线核对,且需相应实时核对平台建设
离线核对(如 T+1 核对)
主要问题是发现问题的时机较为后置,部分场景会影响系统时效性。如清结算与账务侧的每日资金核对失败会影响结算时效性
2.1 一致性核对
资金在从业务端起点(数据由业务产生)到财务端终点(最终流入财务系统)中,在链路中的各个系统/表中都留有相应凭证。
如交易一笔订单的实付金额对应支付的一笔支付单的支付金额,商户一笔收单或支付退款会在对应商户待结算户发生一笔动账,对应在清结算会做一笔有资金方向的清分分录。对这些金额建设相应的一致性核对任务进行核对验证:
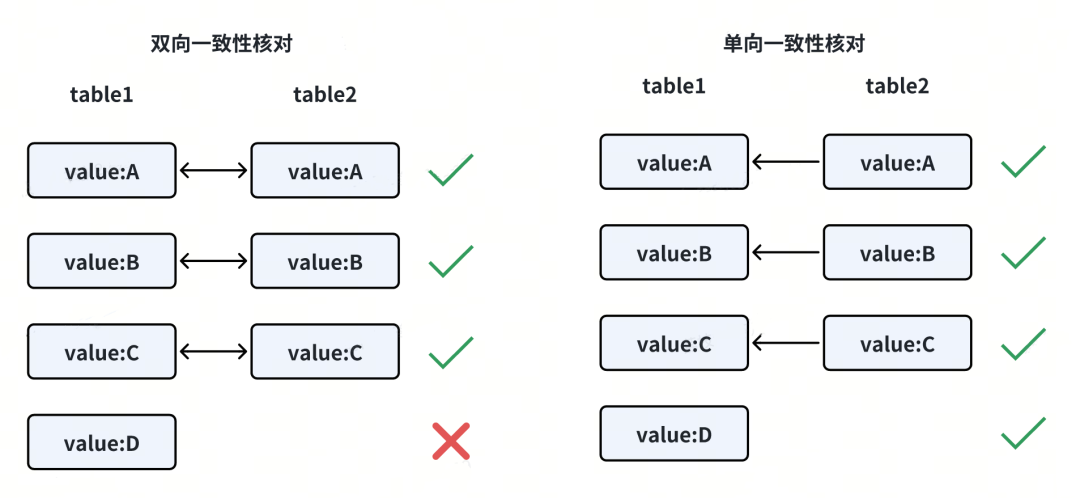
一致性核对包括:
双向一致性核对
单向一致性核对:无法发现单边数据缺失问题。
2.2 业务正确性核对
特定业务场景下,业务有自身业务规则,可针对这些业务规则校验。
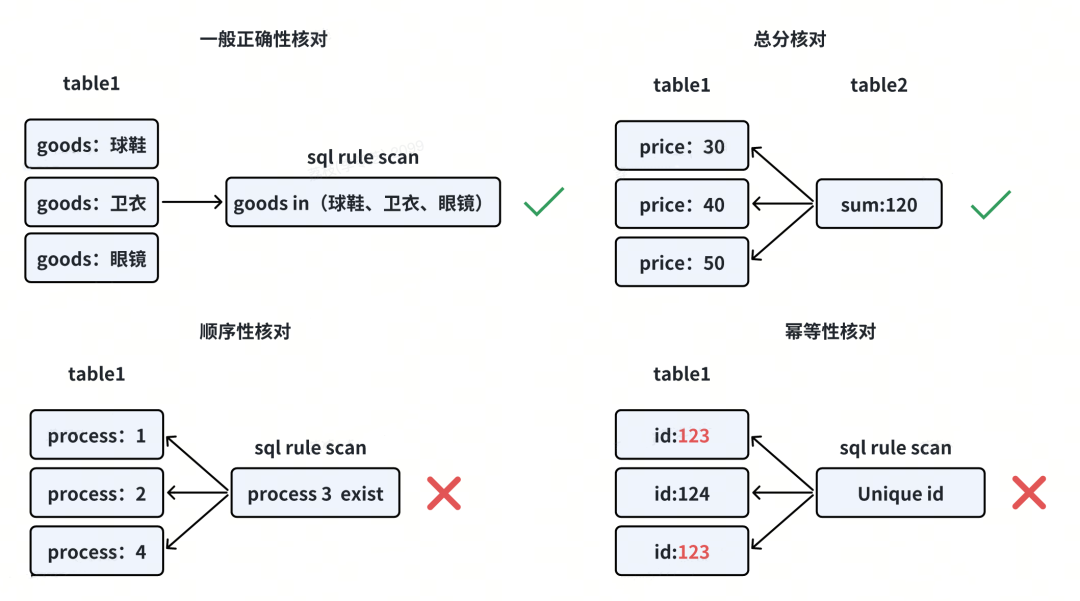
① 一般正确性校验
如某些支付业务只能用于特定商品类型,则可通过自定义SQL校验规则校验。
② 总分校验
各子金额汇总应等于总金额。
③ 顺序性核对
业务流程中有依次执行的处理流程,则可校验是否有流程缺失。
④ 幂等性核对
校验是否有业务被异常的重复处理,如重复退款等。
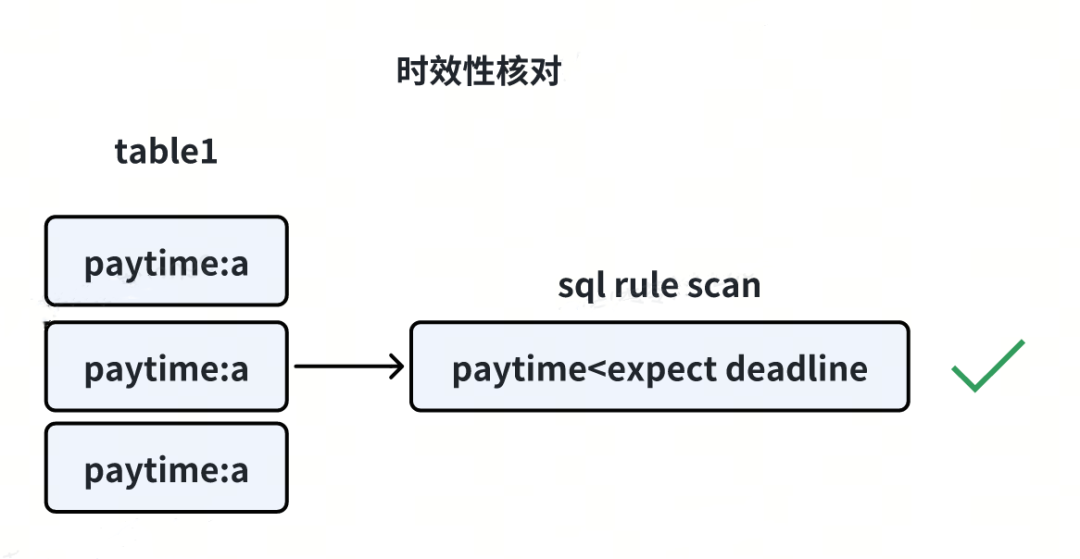
2.3 时效性核对
主要核对时效相关,如未支付的支付单在超时后是否及时关闭,结算时机是否满足时效要求等。
2.4 风险额度核对
对一些可能有高风险的关键配置与金额相关额度进行校验,如分账比例 <=30%、不能负佣、总营销金额不能超过每日上限等。

2.5 小结
- 对实时性较高的任务采用实时核对
- 而日终检查等采用离线核对
通过对支付全过程的监控预警以及失败 case 产研及时介入处理,从而保证了资金安全准确性。
关注我,紧跟本系列专栏文章,咱们下篇再续!
作者简介:魔都国企技术专家兼架构,多家大厂后台研发和架构经验,负责复杂度极高业务系统的模块化、服务化、平台化研发工作。具有丰富带团队经验,深厚人才识别和培养的积累。
参考:
- 编程严选网
本文由博客一文多发平台 OpenWrite 发布!
