安阳市建设工程招标投标协会网站网站建设中期检查表怎么写
命令行: kubectl命令行工具
优点: 90%以上的场景都可以满足
对资源的增,删,查比较方便,对改不是很友好
缺点:命令比较冗长,复杂难记
声明方式:k8s当中的yaml文件实现资源管理----声明式
GUI:图形化工具的管理。
查看k8s的版本
kubectl version
查看k8s的集群信息
kubectl cluster-info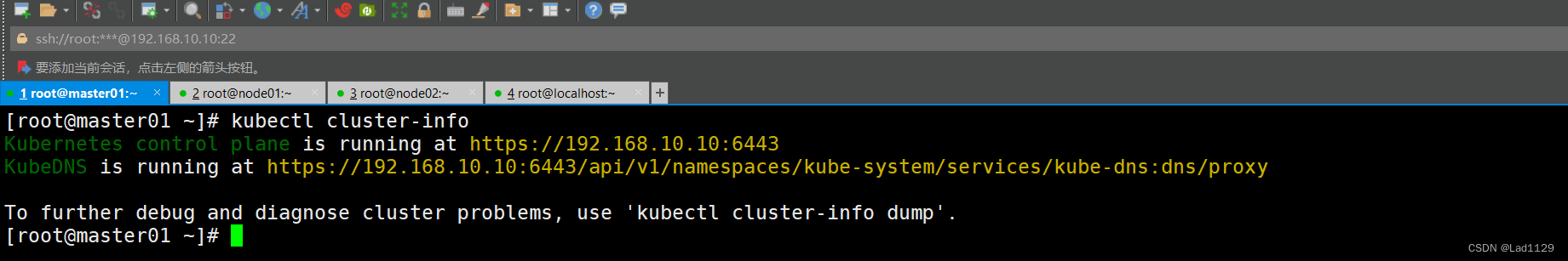 查看所有api的资源对象的名称。
查看所有api的资源对象的名称。
kubectl api-resources
查看当前master的节点状态
kubectl get cs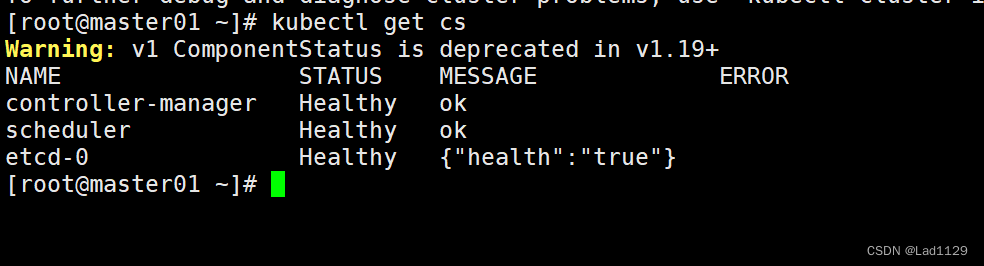
查看默认命名空间内的的pod的信息
kubectl get pod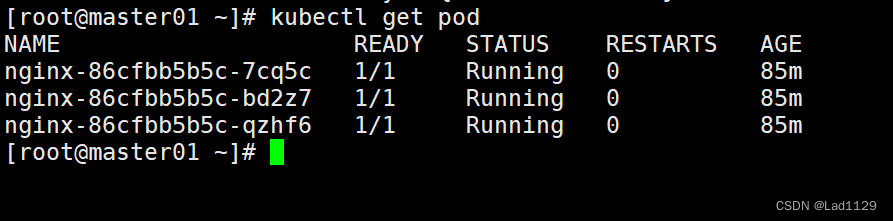
查看当前集群所有的命名空间
kubectl get ns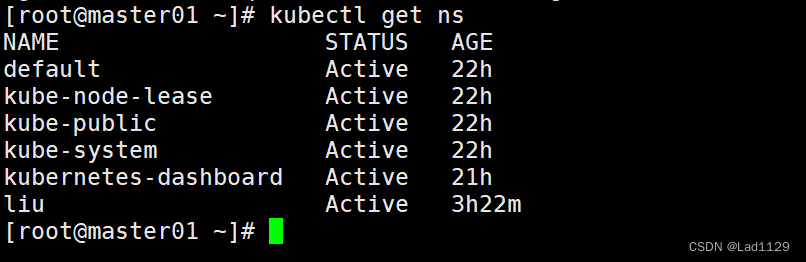
要查看指定命名空间内的pod需要加-n 命名空间的名称
kubectl get pod -n kube-system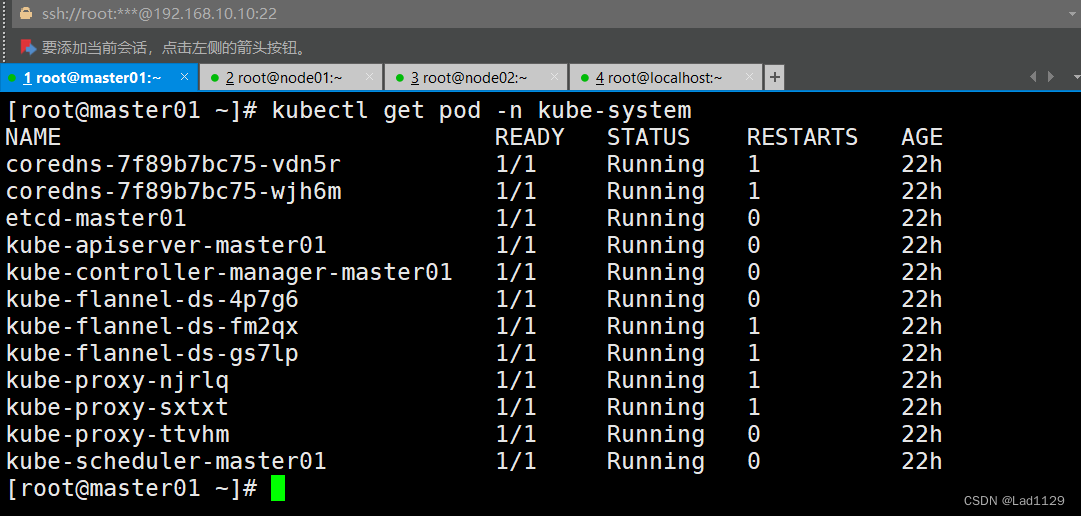
查看默认命名空间内pod的详细信息
kubectl get pod -o wide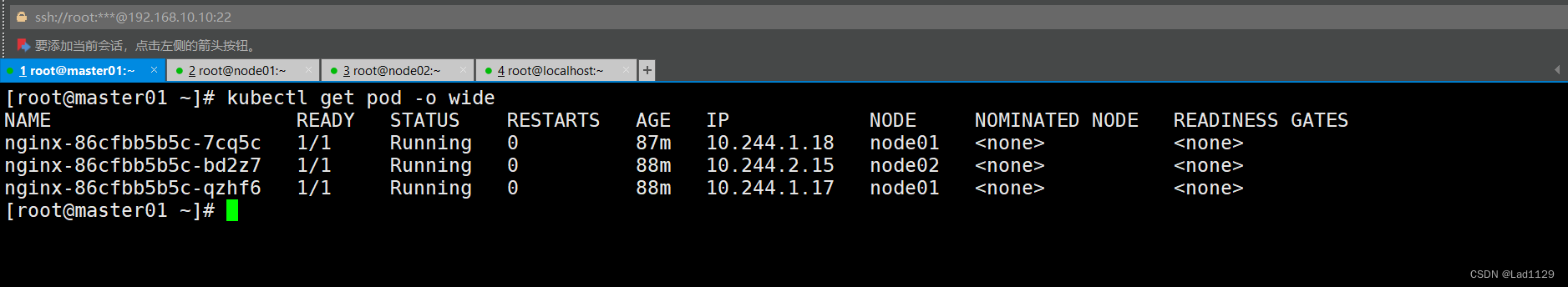
查看指定命名空间的详细信息
kubectl get pod -o wide -n kube-system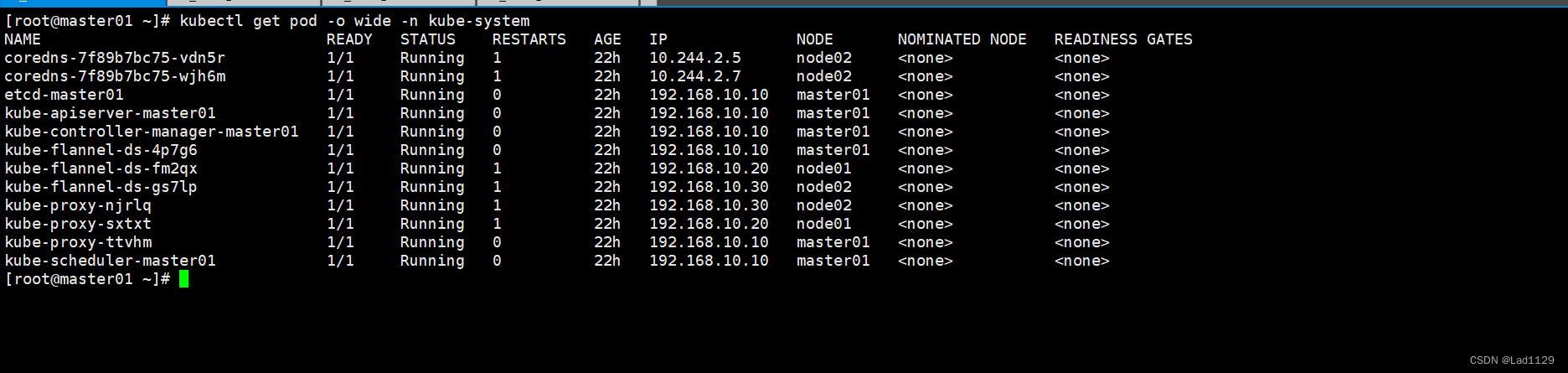
查询节点的信息和状态
kubectl get node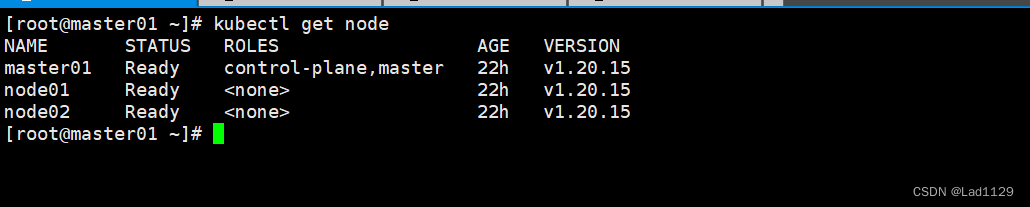
查看node节点的详细信息
kubectl get node -o wide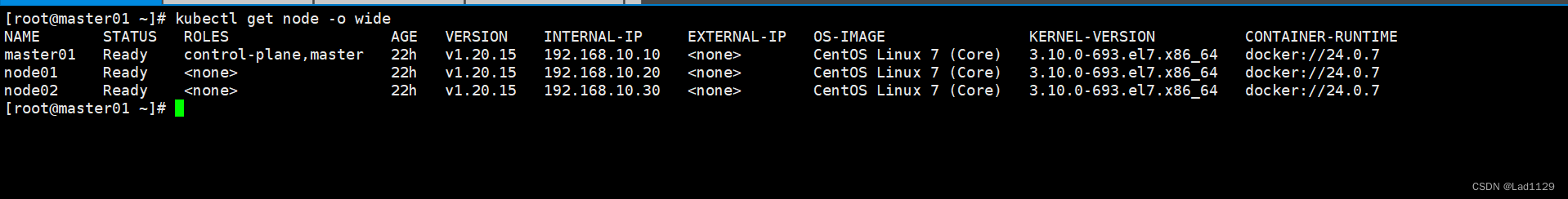
查看已经部署好的pod详细信息
kubectl get pod
kubectl describe pod nginx-86cfbb5b5c-qzhf6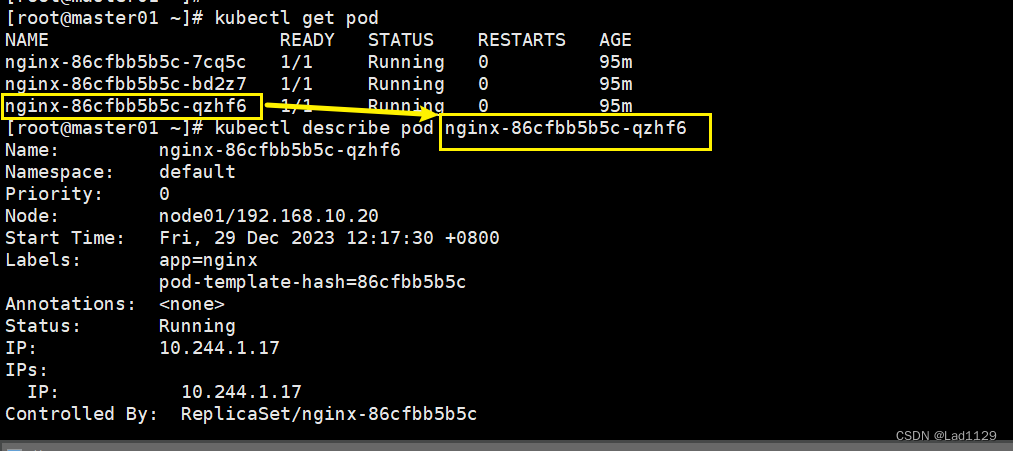
创建命名空间
kubectl create ns guoqi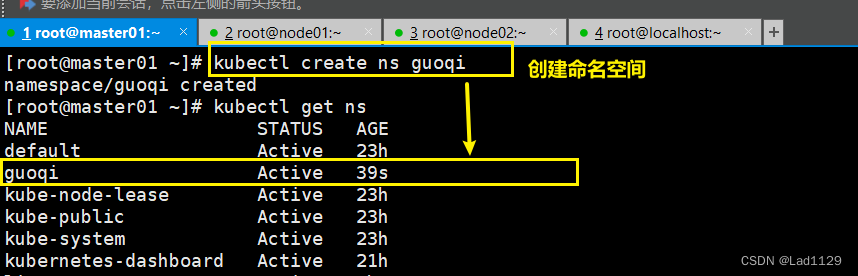
删除命名空间
kubectl delete ns guoqi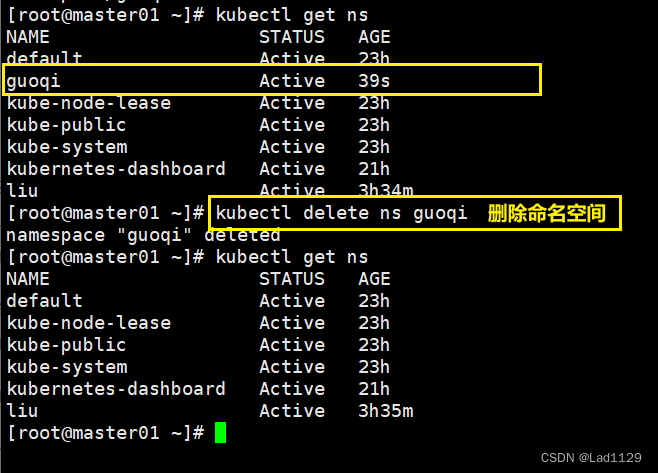
删除pod中的容器
不是真正的删除,是重启容器
kubectl delete pod nginx-6799fc88d8-fb64x(pod名称)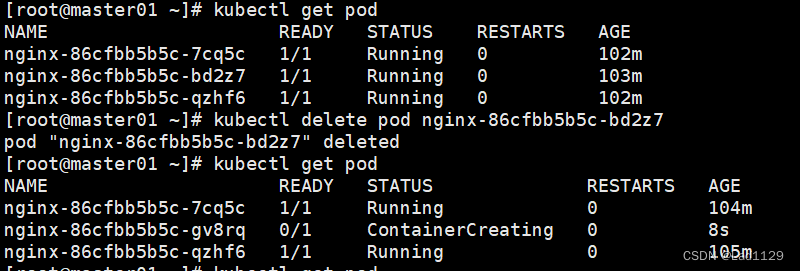
立刻停止pod
主要是用于结束卡在销毁状态的pod
kubectl delete pod nginx-6799fc88d8-7p2t9 --force --grace-period=0
#--grace-period:过度的存活期。默认是30秒。可以让pod优雅的结束容器内的进程,然后退出pod
#=0:表示立即停止pod。必须要force实现。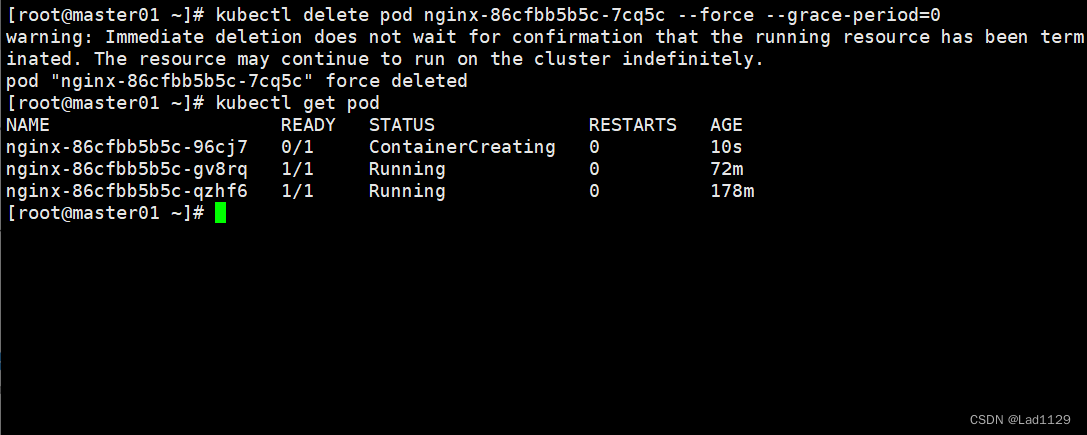
如果是基于deployment方式创建的pod或者是daemonset方式创建的pod,是由控制器创建的pod,使用delete删除pod是不删不掉的,相当于重启pod.
要删除基于控制器创建的pod,一旦删除deployment,基于这个deployment创建的pod会被删除。
deployment的部署pod
陈述式部署:命令行
声明式: yaml文件部署
下述的功能必须是基于deployment创建的服务才可以。
| 滚动更新 | 不是一次性的把所有pod全部部署,而是一个个来。pod的更新时使用,逐步的引入新的pod.逐步的减少旧的pod |
| 自我修复 | 如果有pod节点发生故障,deployment会自动启动新的pod来进行代替 |
| 回滚 | 如果更新有问题,deployment会提供还原点,可以手动还原到未更新的状态。 |
| 扩容和缩容 | deployment可以随时调整pod的数量,以适应流量的变化。 |
查看默认命名空间
kubectl get deployments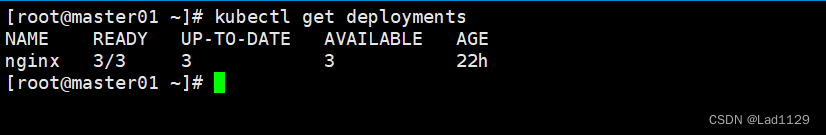
查看指定命名空间
kubectl get deployments.apps -n kube-system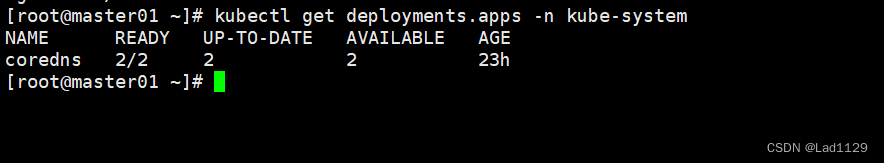
daemonset
daemonset:不能通过命令行创建,只能通过yaml的创建daemonset,后台运行创建,只能在每个节点创建一个相同方式的,相同版本的容器运行的pod,一般都是依赖环境和重要组件,一般也不会去对这些进行操作。
指定副本数
kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx --replicas=3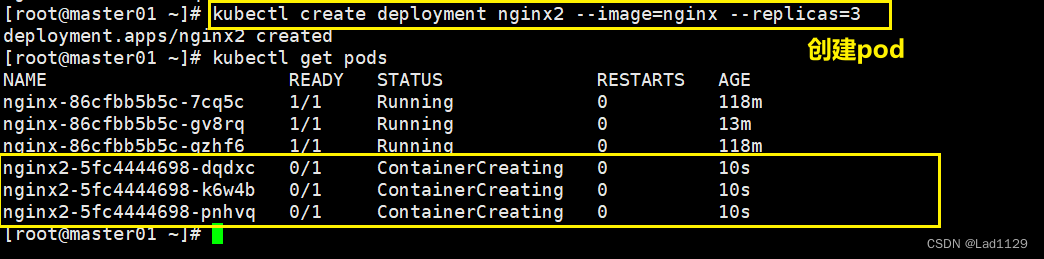
指定deployment命名空间
kubectl create ns liu
kubectl create deployment nginx-liu --image=nginx --replicas=3 -n liu
kubectl get pod
kubectl get pod -n liu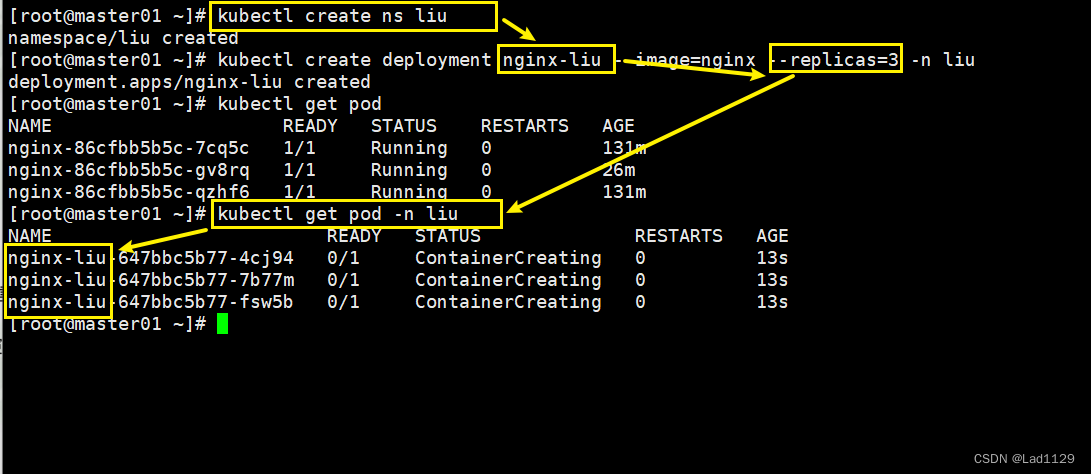
基于run创建的pod
不是基于控制器创建,会被直接删除。
kubectl run --image=nginx liu
kubectl delete pod liu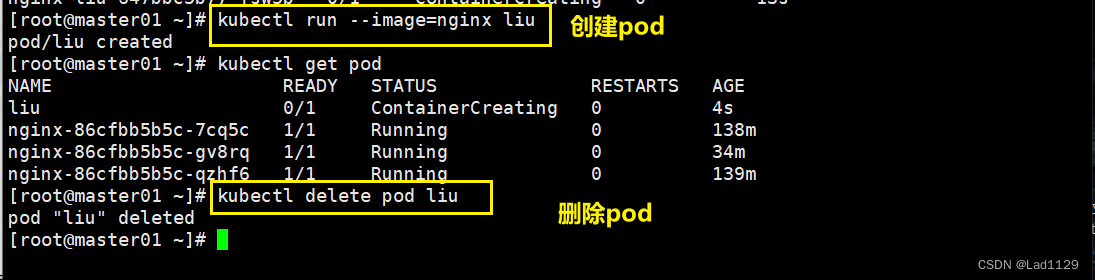
在master节点进入node的容器
进入默认模式的容器
kubectl exec -it nginx-86cfbb5b5c-7cq5c bash
#docker的exec只能在本机内部使用,不能跨主机。kubectl的exec可以跨主机进入容器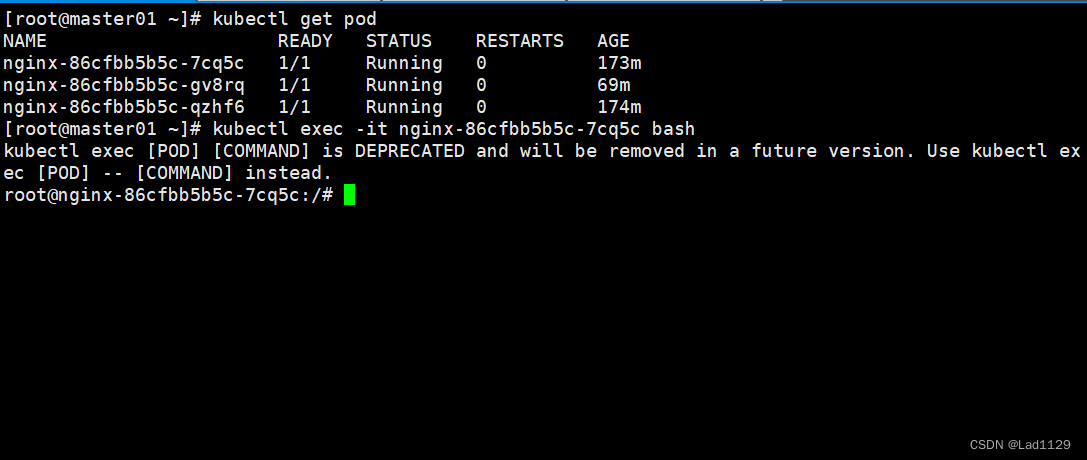
进入指定节点的容器
kubectl exec -it nginx-liu-647bbc5b77-7b77m bash -n liu
#远程进入指定命名空间内的pod节点容器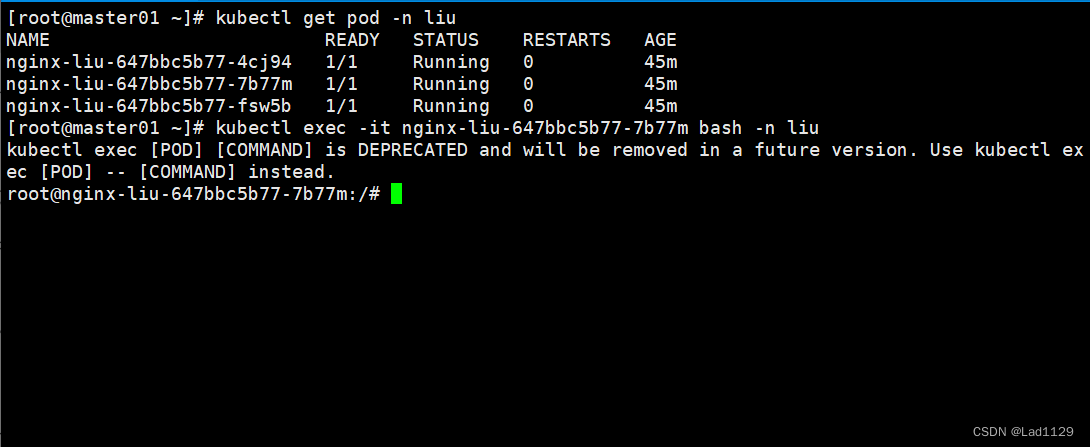
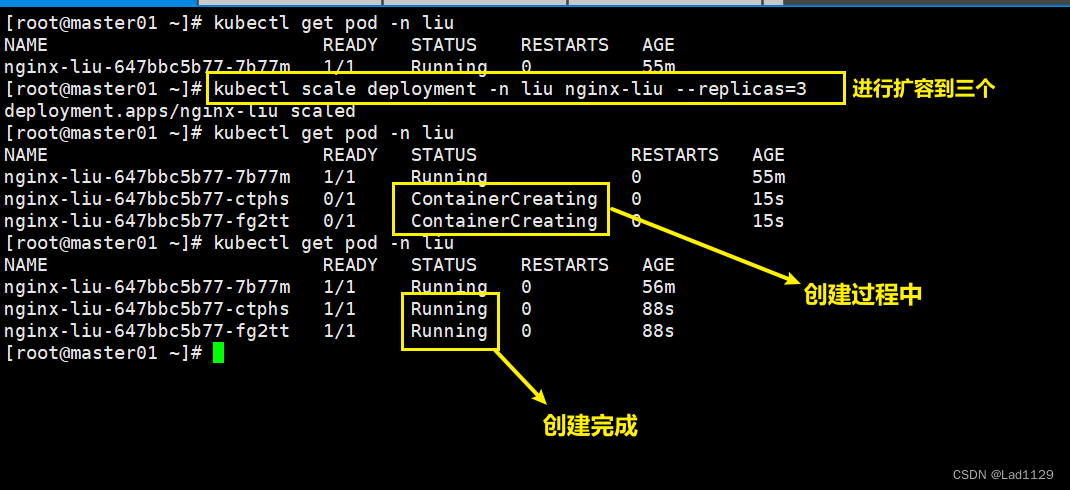
对deployment创建的pod进行扩缩容
扩容
kubectl scale deployment -n liu nginx-liu --replicas=2
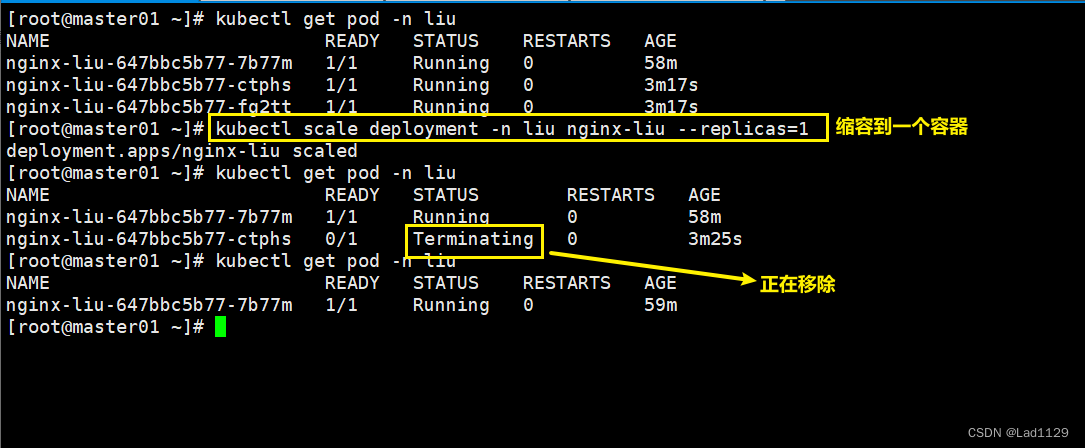
缩容
kubectl scale deployment -n liu nginx-liu --replicas=1server的类型
ClusterIP
ClusterIP:server时默认类型,提供一个集群内部的虚拟ip地址,这是service的默认类型。通过这个虚拟ip可以直接访问pod资源,无法对外提供访问。
NodePort
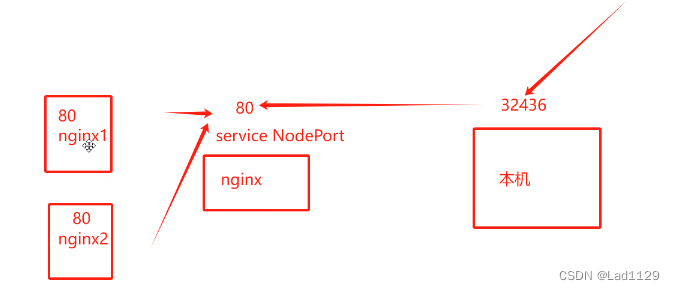
NodePort:会在每个node节点上都开放一个相同的端口,外部可通过node的本机ip+端口,防护pod资源。集群外部访问service资源的一种方式,四层代理代理。
nodeip:nodeport
会随机指派,也可以指定。
端口会从30000-32767的固定范围随机指派一个端口,或者可以指定一个这个范围内的端口。
基于deployment创建的pod可以使用的pod可以使用方式:
kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --target-port=80 --name=nginx-service --type=NodePort
--port=80 service集群的端口
--target-port=80 pod内部容器的端口
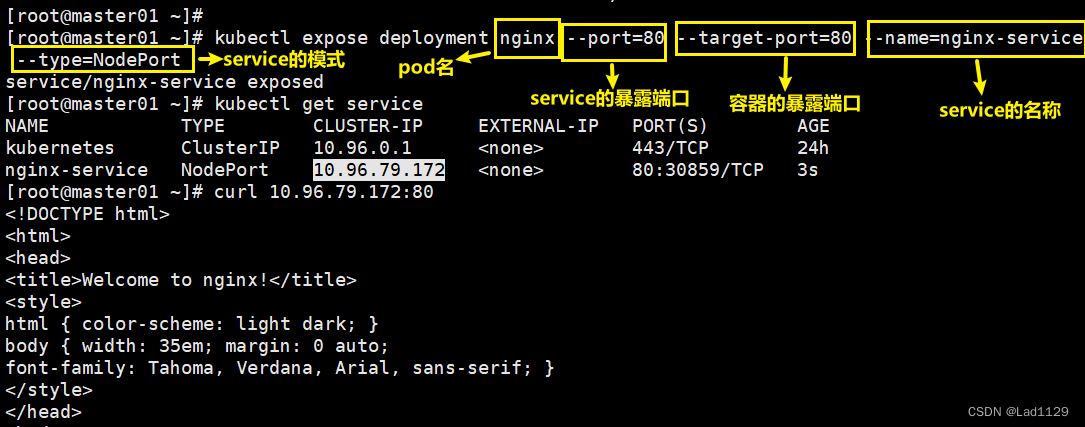
10.96.79.172 集群内部的ip地址,外部是不可以访问这个ip地址的
80: 对应的是内部的service的端口
30859: 和内部的service的80端口做映射(30000-32767)
端口映射关系
修改本机
kubectl edit svc nginx-service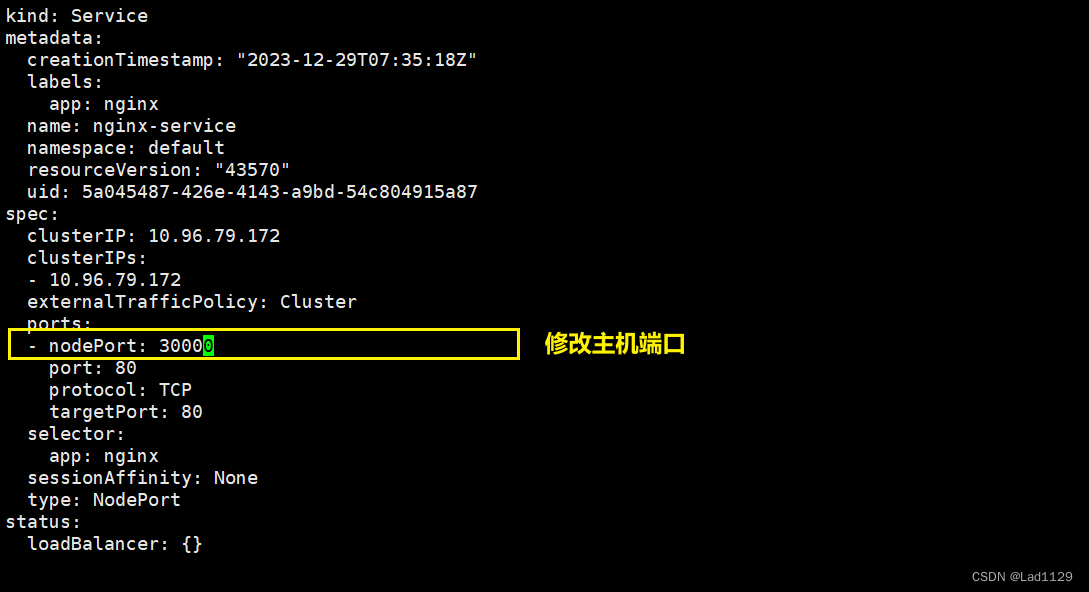
LoadBalancer
如果service的类型设定为LoqdBalancer,映射地址(云平台提供LoadBalancer的地址)这种用法仅限于公有云服务供应商在云平台上设置的service的场景,外部来访问,实现外来访问,实现负载均衡。LoadBalancer这个地址是要付费的。
创建service,指定类型为LoadBalancer,会给你提供一个地址来带代理pod内部的ip地址。
kubectl expose deployment nginx1 --port=8080 --target-port=80 --name=nginx2-server --type=LoadBalancer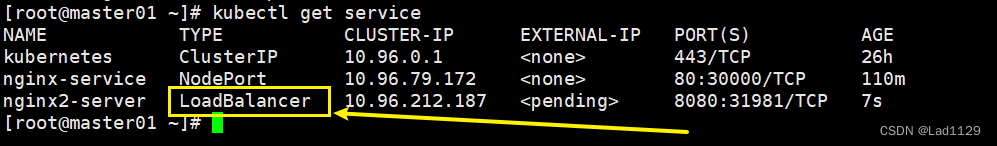
ExternalName
ExternalName:DNS映射,给service分配一个域名来访问后端pod资源。ExternalName的service类型,不能提供负载均衡,必须要设置一个LoadBalancer的地址才可以实现。
kubectl edit svc nginx1-server
#进入service内直接修改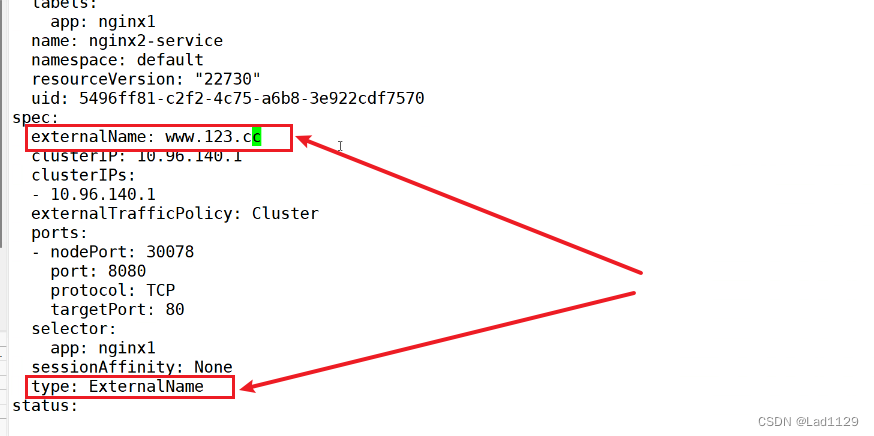
vim /etc/hosts
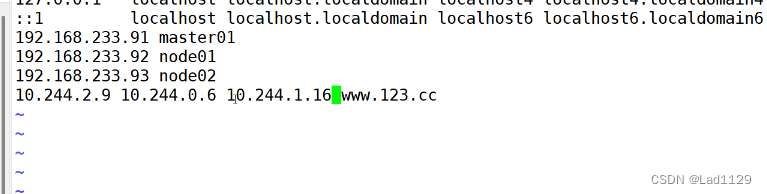
需要在hosts里做映射
四个类型我都知道
默认类型只对内访问
NodePort类型我配置过可以对外访问
LoadBalancer类型需要花钱
ExternalName类型需要配置域名
更新和回滚以及发布的方式
项目的生命周期:
创建------------发布------------更新----------回滚------------删除
滚动更新:
无标志更新
kubectl set image deployment nginx nginx=nginx:1.22.0
#滚动更新服务的版本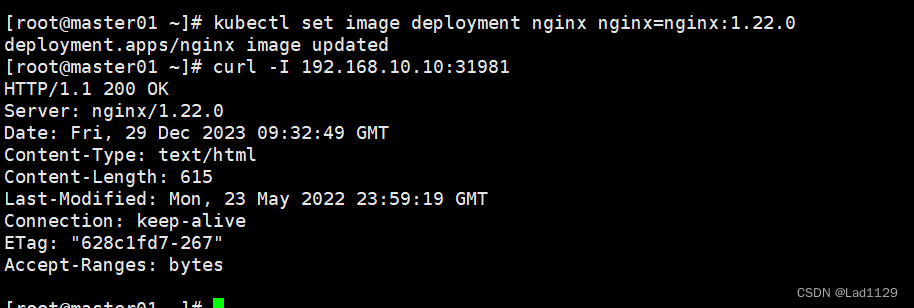
增加回滚点标识
先把新的pod拉起来,在把旧的版本删掉
kubectl set image deployment nginx nginx=nginx:1.22.0 --record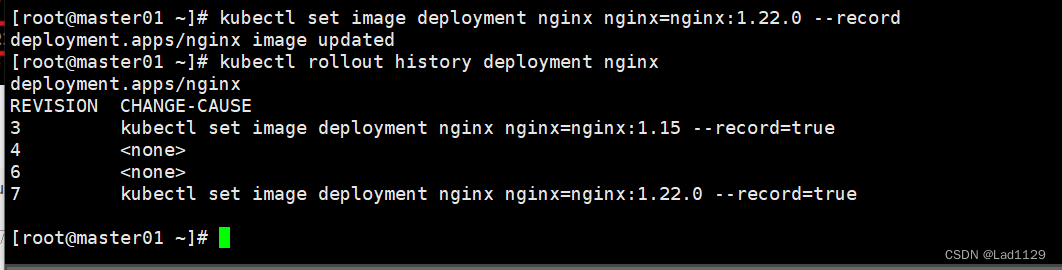
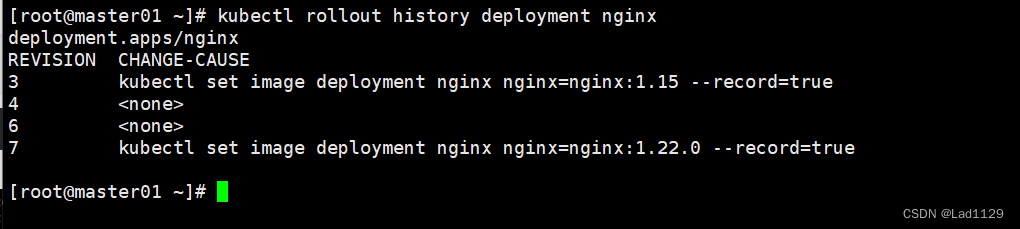
查看更新历史操作
kubectl rollout history deployment nginx
#查看回滚点信息
#数字的大小决定了距离上次操作的远近。数字越大就是最近的一次操作
回滚点
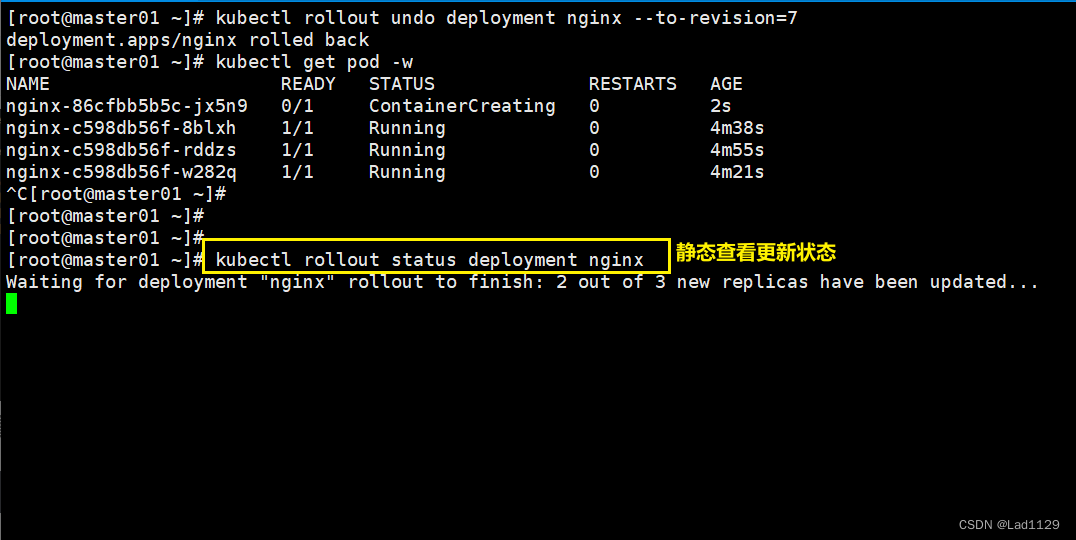
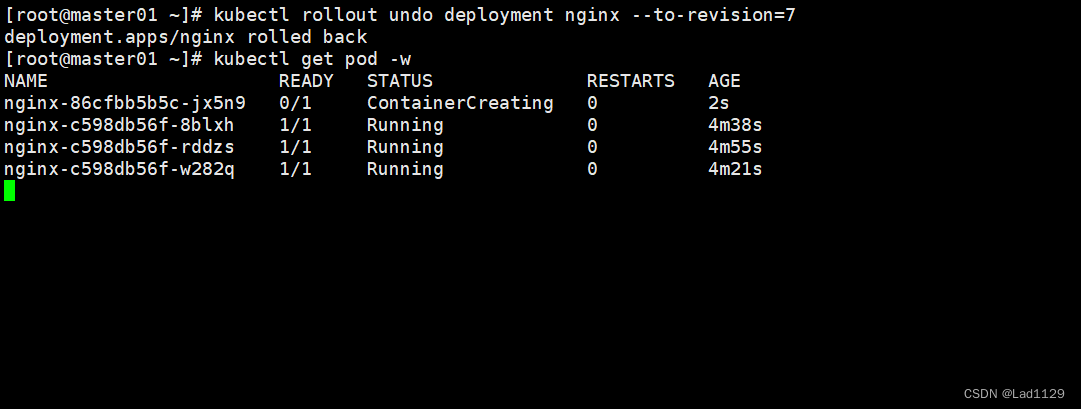
kubectl rollout undo deployment nginx --to-revision=1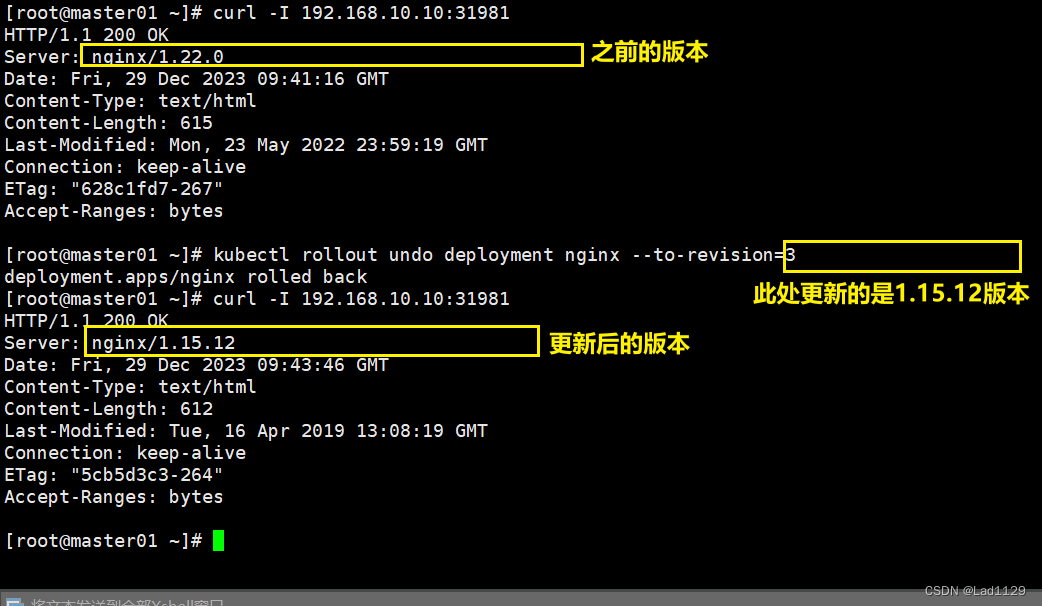
动态查看更新动态
kubectl get pod -w静态查看
kubectl rollout status deployment nginx